
- #Overflow incontinence. full
- #Overflow incontinence. series
Next, they will likely perform a thorough physical exam, which may focus on the abdomen to feel for an enlarged bladder, as well as a rectal or pelvic exam.
They may also ask a person to keep a voiding diary.
#Overflow incontinence. series
They may also ask a person to fill out a questionnaire or answer a series of questions about fluid intake, bowel habits, and any other urinary symptoms. Typically, a doctor will review a person’s medical history to identify any conditions, past surgeries, or other possible causes that could contribute to incontinence. While many types of urinary incontinence are typically more prevalent in females, overflow incontinence occurs more often in males, particularly those with prostate problems or who have had prostate surgery. A 2016 study found that people taking atypical antipsychotics experience similar bladder dysfunction to those with neurological conditions.
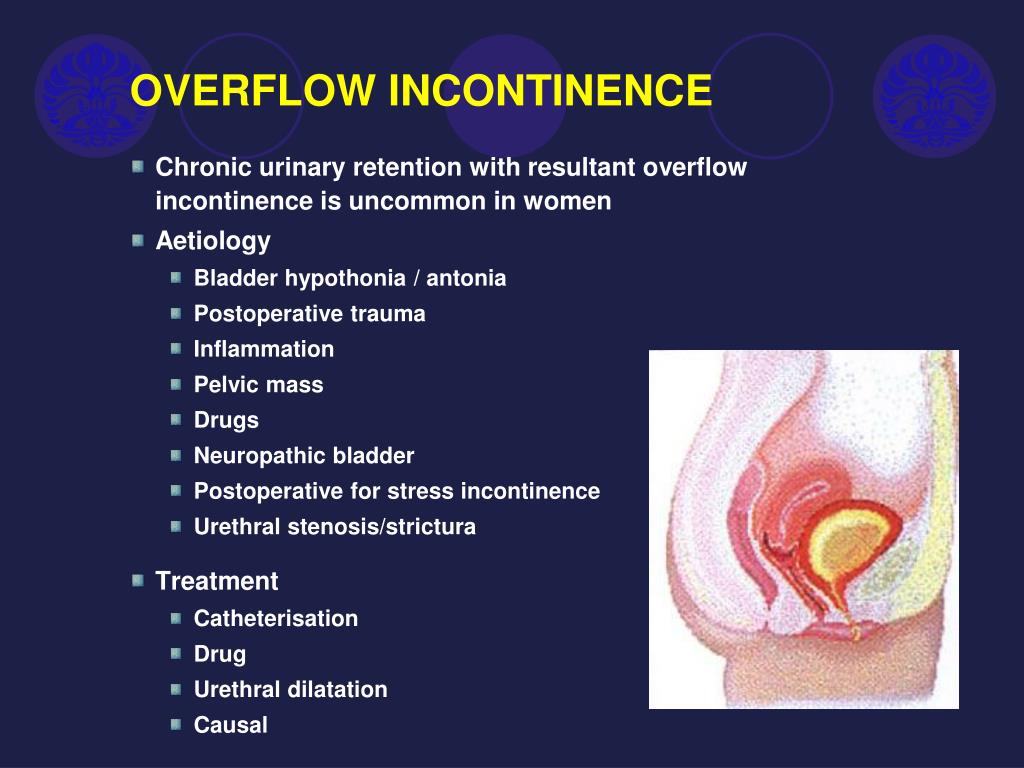
Certain medications: Some medications may cause the bladder to overfill. In males, it can also occur due to an enlarged prostate, prostate cancer, and past surgery. Blockages can include bladder stones, constipation, and narrowing of the urethra. A blockage anywhere in the urinary tract: Obstructions can make it difficult to empty the bladder. Muscle damage: Similarly, damage to the bladder and its muscles may mean the bladder cannot empty fully. #Overflow incontinence. full
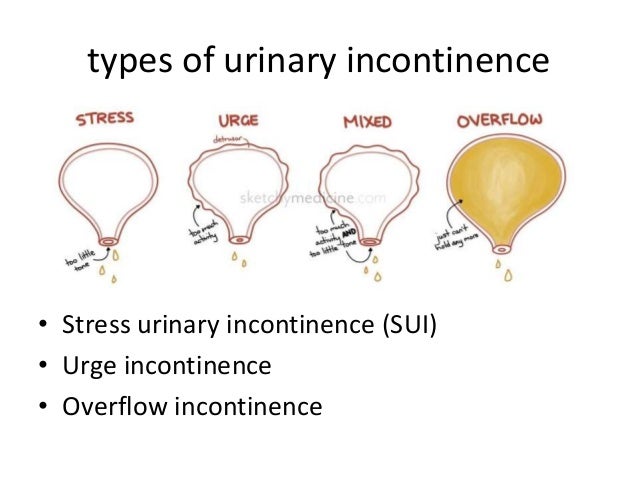
Nerve damage: Injury, surgery, or conditions such as MS, Parkinson’s disease, and spina bifida can affect the nerves, altering the person’s ability to sense a full bladder or reducing the bladder’s ability to contract. Weakness of bladder muscles: If the muscles that control urination cannot squeeze the bladder correctly, it can cause difficulty emptying the bladder. Overflow incontinence happens when the bladder retains too much urine due to problems preventing it from emptying.  Functional incontinence: This type of incontinence involves physical and environmental barriers, such as lacking access to a toilet. Reflex incontinence is related to a neurological cause or injury, and typically a person with this type may experience a void of their entire bladder contents without warning. People have involuntary muscle contractions even if they do not feel any urge to urinate. However, this type of incontinence causes more leakage. Reflex incontinence: Similar to urge incontinence, bladder spasms cause this incontinence. It is more common in females, but may also occur in males who had their prostate removed or have undergone surgery for a large prostate. Mixed incontinence: This type is a combination of urge and stress incontinence. This can result from problems with involuntary muscle contractions and is common in people with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis (MS).
Functional incontinence: This type of incontinence involves physical and environmental barriers, such as lacking access to a toilet. Reflex incontinence is related to a neurological cause or injury, and typically a person with this type may experience a void of their entire bladder contents without warning. People have involuntary muscle contractions even if they do not feel any urge to urinate. However, this type of incontinence causes more leakage. Reflex incontinence: Similar to urge incontinence, bladder spasms cause this incontinence. It is more common in females, but may also occur in males who had their prostate removed or have undergone surgery for a large prostate. Mixed incontinence: This type is a combination of urge and stress incontinence. This can result from problems with involuntary muscle contractions and is common in people with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis (MS). 
Overactivity of the bladder muscles often causes this. This occurs even if the bladder is not full. Urge incontinence: This is when a person suddenly feels a strong urge to urinate but cannot hold their urine long enough to reach the toilet.Pregnant people and those who have given birth vaginally may be at a higher risk of this type of incontinence. This may be due to a weak urethral sphincter, pelvic floor muscles, or both. Stress incontinence: This refers to when a person experiences increased abdominal pressure on the bladder from sneezing, coughing, or exerting effort, which causes urine to leak.
Each type differs in its cause and presentation. Overflow incontinence is one of the several types of urinary incontinence. How it differs from other types of incontinence








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
